The human pressure characterized by increasing urbanization, conversion of habitats to small-scale farms and industrial scales through land grabbing and acquisition of forestry operations at different scales accelerate habitat fragmentation and prevent migration of northern wildlife of Cameroon, in eastern Cameroon, chimpanzees and forest elephants from Africa.
It is within this context of ecological fragmentation and disintegration that the preventing species Inbreeding and Local Extinction Project (PSILC Project Cameroon) is being conceived by Erudef Cameroon. PSILE Project would be located in three sites namely:
– Western Cameroon with focus on Cross River Gorillas, Africa Forest Elephant and Nigeria-Cameroon Chimpanzees
– Western lowland gorillas, Africa Forest elephants and central chimpanzees in Eastern Cameroon and
– The large cats and savannah elephants in Northern Cameroon.
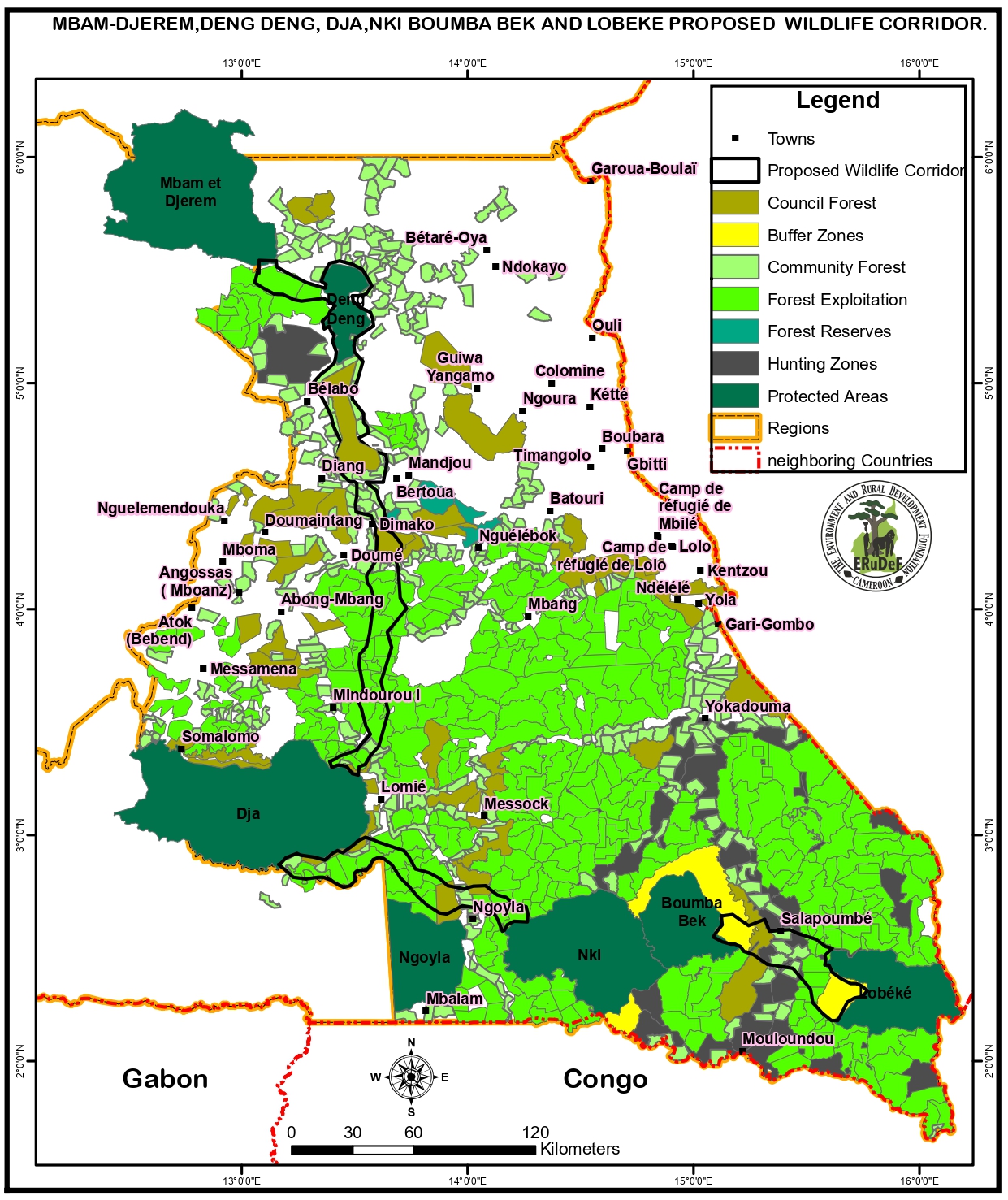
For each of the sites, the current and existing ecological and migration corridors would be investigated mapped and protected through the creation of community forests. Community forests are best forms of land acquisitions that local communities would be most ready to welcome.
The specific objectives of the project would include.
– To map and establish the migratory sites for the migratory species through the use of GIS and Remote Sensing
– To support the creation and management of community forests and other sustainable land use forms acceptable to the local community and stakeholders.
– To set up a community-based tourism to increase the economic and financial value of the key wildlife species being supported in the ecological corridors.
– To facilitate the creation and operationalisation of the community forestry fund for local Community Development (CFFLCD) as a long term financial funding mechanism to support the financing of the ecological corridors and community forests along the ecological corridors.
And the intended impacts are:
– The Eastern Cameroon ecological corridor of over 700000ha would be secured linking three key protected areas of Mbam Djerem National Park, Deng Deng National Park and Dja Biosphere Reserve
– In Western Cameroon, ecological corridor of over 50000ha would be secured linking Tofala Hill Wildlife Sanctuary (30 Cross River gorillas), Mwambi Hills (20 Cross River gorillas). Takamanda NP (100 Cross River gorillas) and Kagwane Gorillas Sanctuary (20 Cross River gorrilas) would be saved from being trapped to inbreeding and sites extinction in Cameroon.

Commentaires récents